digital amputation procedures
Preventing symptomatic neuroma after digital amputation can be difficult due to the limited musculature in the hand, which can result in mechanical stimulation of the nerve end.
Traumatic injuries to the hand and fingers are common reasons for emergency room visits, and it has been reported they result in as many as 27,000 amputations annually in the U.S.1 The management of symptomatic neuromas after digital amputations can have significant implications on a patient’s ability to use their hand.
Axoguard Nerve Cap® provides an environment for the nerve end that is protected from mechanical stimulation and isolated from neurotrophic factors. The proprietary bifurcation provides adequate space for regenerating axon growth to exhaust and helps reduce symptomatic neuroma formation.2
remember the following:
- It is reported only 33%–40% of patients were satisfied with treatment after burial into bone or muscle.3
- Simply burying the nerve into the intrinsic muscles in the hand can result in pain due to muscular contraction or localized pressure.4-6
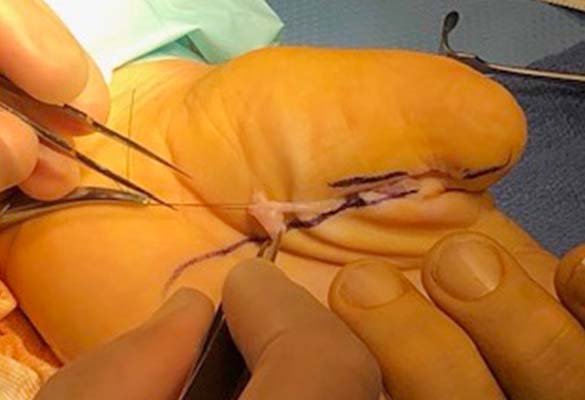
The patient had increasing hypersensitivity after traumatic amputation of the left thumb, until a resection of two digital nerve neuromas, one recurrent, with the placement of Axoguard Nerve Cap was successfully performed. Case Courtesy of Mark S. Rekant, M.D., Philadelphia Hand to Shoulder Center.
view case studymore procedures
There’s only a short form between you and our nerve product team who can help you get more information about our nerve repair solutions.
references
- Reid DBC, et al. Epidemiology of finger amputations in the United States from 1997 to 2016. J Hand Surg Glob Online. Apr 2019;1(2):45-51.
- Tork S, et al. Application of a porcine small intestine submucosa nerve cap for prevention of neuromas and associated pain. Tissue Eng Part A. May 2020;26(9-10):503-511.
- Stokvis A, et al. Surgical management of neuroma pain: a prospective follow-up study. Pain. Dec 2010;151(3):862-869.
- Regal S, et al. Surgical management of neuromas of the hand and wrist. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. May 2019;27(10):356-363.
- Eberlin K, et al. Surgical algorithm for neuroma management: a changing treatment paradigm. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2018;6(10):E1952.
- Wu J, et al. Painful neuromas: a review of treatment modalities. Ann Plast Surg. Dec 1999;43(6):661-667.