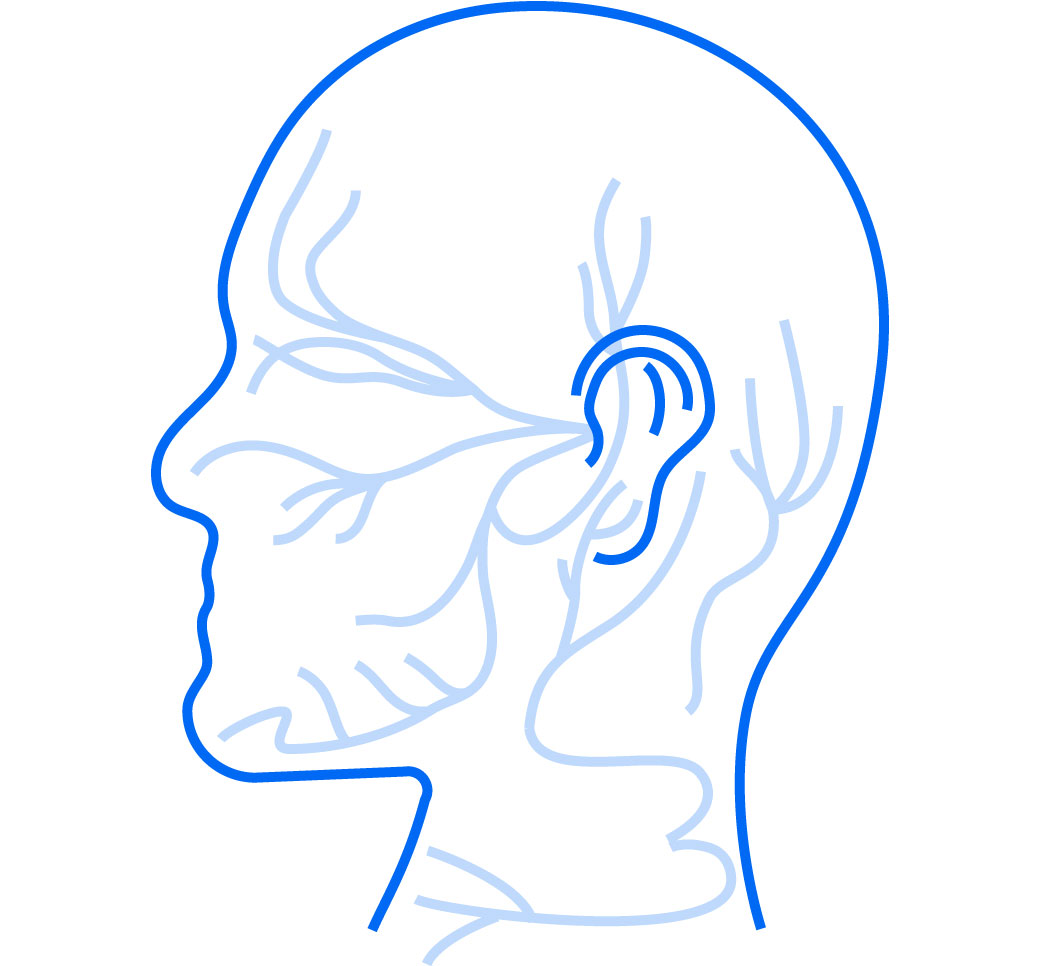
nerve deficits can reduce patient life satisfaction by 28%1
Nerve repair during mandibular resection can help save patients a lifetime of struggle with sensation loss.2,3
How does restoring sensation impact patients?
For patients who underwent nerve reconstruction, they’re very happy when they get sensation back. When that sensation starts to return, it’s all they talk about.
— PATRICK B. GARVEY, MD, FACS
We get it. Nerve function isn’t always on the priority list in a complex procedure like mandible resection. But with a few minutes of advance planning paired with your microsurgical skills, reconstructing the nerve can fit into your surgical plan with minimal disruption.
A minimal addition to your procedure can help save patients from permanent nerve deficits, lost function and chronic pain.3,5,6

positively impacts patients’ lives
Surgeons report that patients’ demeanor and outlook on life noticeably improves when sensation returns.7

adds minimal surgical time
With advance planning, sensory restoration can be integrated into the surgical plan with minimal additional time once it becomes part of the routine.

can be performed in patients undergoing radiation
Postoperative treatment with radiation therapy does not impact nerve sensory recovery.6
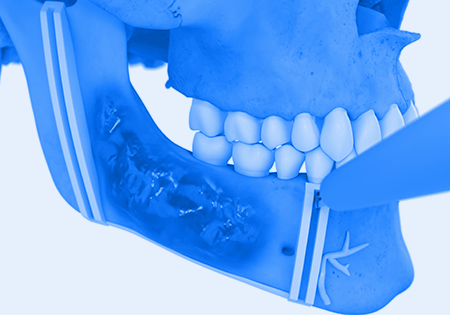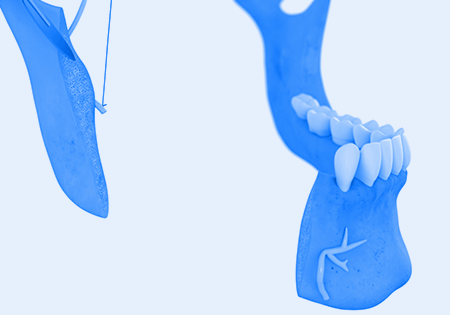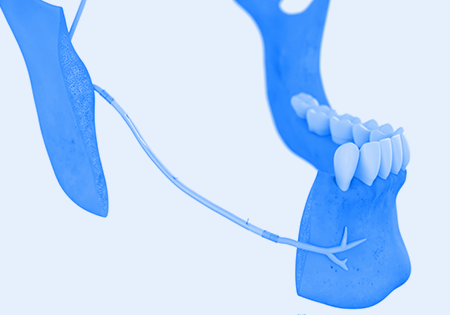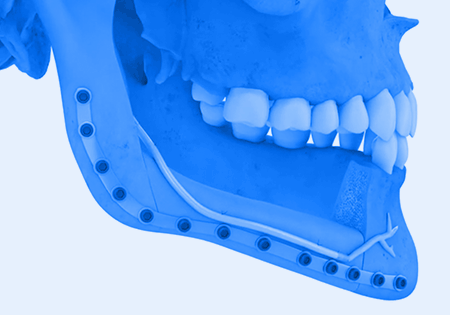
Reconstructing a resected nerve to help patients avoid a potential lifetime of nerve-related symptoms
If we resect a nerve and don’t reconstruct it, there are neuromas or scars that can form on each of the nerve stumps. And those neuromas can be painful; they can cause numbness. They can cause burning and a variety of other painful symptoms, and these patients would have to endure that for the rest of their lives.
— MICHAEL MILORO, DMD, MD, FACS
Why restore sensation?
You have the ability to potentially give this person back sensation with a minimal amount of your time. It changes that person’s life forever.
— JAMES C. MELVILLE, MD, FACS
Nerve reconstruction has the potential to restore pre-surgical levels of sensation3—helping patients regain lost function.
89%
Nearly 90% of study participants (n=18) who underwent inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) reconstruction achieved functional sensory recovery within one year.3
6x
Study patients who underwent nerve repair were 6x less likely to experience chronic post-surgical pain.5
6 months
Six months after IAN reconstruction, all study participants (n=18) who underwent mandibular surgery and reconstruction with processed nerve allograft repair reported no unpleasantness from altered sensations.3
SOLUTIONS
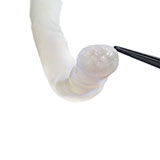 Avance Nerve Graft®
Avance Nerve Graft®  Axoguard Nerve Connector®
Axoguard Nerve Connector®  Axoguard Nerve Protector®
Axoguard Nerve Protector®  Axoguard HA+ Nerve Protector® See sizing and IFU on solution pages.
Axoguard HA+ Nerve Protector® See sizing and IFU on solution pages. There’s only a short form between you and our nerve product team who can help you get more information about our nerve repair solutions.
references
- Leung YY, et al. Trigeminal neurosensory deficit and patient reported outcome measures: the effect on life satisfaction and depression symptoms. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e72891. Published 2013 Aug 29. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0072891
- Zuniga JR. Sensory outcomes after reconstruction of lingual and inferior alveolar nerve discontinuities using processed nerve allograft–a case series. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;73(4):734-744. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2014.10.030
- Zuniga JR, et al. A case-and-control, multisite, positive controlled, prospective study of the safety and effectiveness of immediate inferior alveolar nerve processed nerve allograft reconstruction with ablation of the mandible for benign pathology. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;75(12):2669-2681. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2017.04.002
- Patel N, et al. Quality of life following injury to the inferior dental or lingual nerve – a cross-sectional mixed-methods study. Oral Surg. 2018;11:9-16. https://doi.org/10.1111/ors.12259
- Zuniga JR, et al. Does immediate long-span nerve allograft reconstruction affect the incidence of chronic postsurgical and neuropathic pain in the reconstructed mandible following resection for benign and malignant disease. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2023;81(12):1587-1593. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2023.09.00
- Kaplan J, et al. Sensory outcomes for inferior alveolar nerve reconstruction with allograft following free fibula mandible reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2023;152(3):499e-506e. doi:10.1097/PRS.0000000000010286
- Axogen data on file.
- Lans J, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of nerve gap repair: comparative effectiveness of allografts, autografts, and conduits. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2023 May 1;151(5):814e-827e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000010088.
- Raizman NM, et al. Procedure costs of peripheral nerve graft reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2023;11(4):e4908. Published 2023 Apr 10. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000004908
- Safa B, Momeni A. Reconsidering the standard of care for peripheral nerve reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2023;11(11):e5320. Published 2023 Nov 16. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000005320